Enterprise Integration
Integration
NeuVector provides a number of ways to integrate, including a REST API, CLI, SYSLOG, RBACs, SAML, LDAP, and webhooks. See the Automation section for examples of scripting using the REST API.
Integrations with other ecosystem partners such as Sonatype (Nexus Lifecycle), IBM Cloud (QRadar and Security Advisor), Prometheus/Grafana, are also supported. Many of these can be found on the NeuVector Github page.
The following configurations can be found in Settings:
OpenShift/Kubernetes RBACs
Select this option if you are using Red Hat OpenShift Role Based Access Controls (RBACs) and would like NeuVector to automatically read and enforce those. If selected, OpenShift users can log into the NeuVector console using their OpenShift credentials, and will only have access to the resources (Projects, containers, nodes etc) according to their role in the OpenShift cluster. OpenShift integration uses the OAuth2 protocol.

Do not use the setting in OpenShift AllowAllPasswordIdentityProvider which allows any password to be used to log in. This will allow a user to login into NeuVector with any password as well (as a read only user). It will also create a new user in OpenShift for every login (see ‘oc get user’ results).
The default Admin user of NeuVector and any additional users created in NeuVector will still be active with OpenShift RBACs enabled.
Trust External Root CAs with Helm
NeuVector can be configured to trust external root Certificate Authorities (CAs) for secure connections such as LDAPS, OIDC, and registry scanning. This configuration enables trusted communication with external authentication and image registry systems.
When configured through the NeuVector Manager UI, the root CA information is stored directly in the Consul database. No Kubernetes Secret or ConfigMap object is created automatically. As a result, this setting cannot be managed through Helm by default because Helm relies on Kubernetes objects for configuration management.
To configure trusted root CAs, use a custom ConfigMap that provides the CA certificates and enables TLS verification.
Create an override.yaml file that includes your CA certificate and TLS verification settings:
controller:
configmap:
enabled: true
data:
sysinitcfg.yaml: |
cacerts:
- -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIID0zCCArugAwIBAgIU...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
enable_tls_verification: true
Save this configuration as override.yaml, then deploy NeuVector using Helm.
helm install neuvector neuvector/core -n neuvector --set manager.svc.type=NodePort,imagePullSecrets=regsecret -f override.yaml
After deployment, confirm that the configuration is applied by viewing the neuvector-init ConfigMap:
kubectl get cm neuvector-init -o yaml
You should see the certificate block and TLS verification settings reflected in the output.
apiVersion: v1
data:
sysinitcfg.yaml: |
cacerts:
- -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIID0zCCArugAwIBAgIU...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
enable_tls_verification: true
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
annotations:
meta.helm.sh/release-name: neuvector
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: neuvector
creationTimestamp: "2025-07-18T16:23:24Z"
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
chart: core-2.8.7
release: neuvector
name: neuvector-init
namespace: neuvector
resourceVersion: "35282681"
uid: a63f139b-dcaf-43c5-bfba-0094c7d98f65
After Helm installation, verify that NeuVector is running and accessible:
NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get -n neuvector -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" svc neuvector-service-webui)
NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}")
echo https://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT
Open this URl in a browser to access NeuVector Manager UI
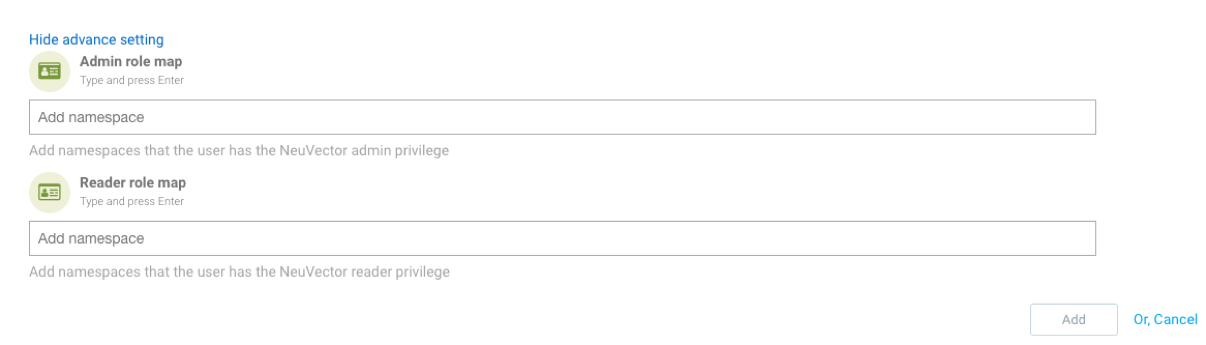
Kubernetes RBACs
To manually configure RBACs for Kubernetes namespaces, open the Advanced Setting in the new user creation screen in Settings -> Users -> Add User. Here you can enter the namespaces(s) which this user should have access to in NeuVector.
SYSLOG
Enter the SYSLOG server IP and select the level of notification. You can also use a DNS name and/or select TCP for configuration.
Webhooks
Notifications can be sent via webhooks to an endpoint. Enter the endpoint URL for notifications to be sent. Webhook notifications for custom events can be configured in Policy -> Response Rules
Directory/SSO Integration
See the next sections for LDAP, MSAD, SAML, OpenId and other integrations. See the Basics -> Users & Roles section for predefined and custom roles in NeuVector which can be mapped in the integration.