Deploy Using Operators
Operators
Operators take human operational knowledge and encode it into software that is more easily shared with consumers. Operators are pieces of software that ease the operational complexity of running another piece of software. More technically, Operators are a method of packaging, deploying, and managing a Kubernetes application.
NeuVector Operators
The NeuVector Operator is based on the NeuVector Helm chart. The NeuVector RedHat OpenShift Operator runs in the OpenShift container platform to deploy and manage the NeuVector Security cluster components. The NeuVector Operator contains all necessary information to deploy NeuVector using Helm charts. You simply need to install the NeuVector operator from the OpenShift embedded Operator hub and create the NeuVector instance.
To deploy the latest NeuVector container versions, please use either the Red Hat Certified Operator from Operator Hub or the community operator. Documentation for the community operator can be found here.
Note about SCC and Upgrading
Privileged SCC is added to the Service Account specified in the deployment yaml by Operator version 1.3.4 and above in new deployments. In the case of upgrading the NeuVector Operator from a previous version to 1.3.4, please delete Privileged SCC before upgrading.
oc delete rolebinding -n neuvector system:openshift:scc:privileged
NeuVector Certified Operator versions are tied to NeuVector product versions, and each new version must go through a certification process with Red Hat before being published. Certified operator version 1.3.9 is tied to NeuVector version 5.2.0. Certified operator version 1.3.7 is tied to NeuVector version 5.1.0. Version 1.3.4 operator version is tied to NeuVector 5.0.0. If you wish to be able to change the version tags of the NeuVector containers deployed, please use the Community version.
Deploy Using Certified Operator
Deploy Using the Red Hat Certified Operator from Operator Hub
NeuVector Operator versions are tied to NeuVector product versions, and each new product version must go through a certification process with Red Hat before being published.
Technical notes
- NeuVector container images are pulled from registry.connect.redhat.com using the RedHat market place image pull secret.
- The NeuVector manager UI is typically exposed via an OpenShift passthrough route on a domain. For example, on IBM Cloud neuvector-route-webui-neuvector.(cluster_name)-(random_hash)-0000.(region).containers.appdomain.cloud. It can also be exposed as the service neuvector-service-webui through a node port address or public IP.
- OpenShift version >=4.6.
Create the project neuvector.
oc new-project neuvectorApply security context constraint (SCC) to grant default service account in neuvector namespace to run privileged containers.
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged --serviceaccount default --namespace neuvectorInstall the RedHat Certified Operator from the Operator Hub
- In the OpenShift Console UI, navigate to OperatorHub
- Search for NeuVector Operator and select the listing without community or marketplace badge
- Click Install
Configure update channel
- Current latest channel is beta, but may be moved to stable in the future
- Select stable if available
Configure installation mode and installed namespace
- Select specific namespace on the cluster
- Select neuvector as installed namespace
- Configure approval strategy
- Confirm Install
Prepare the YAML configuration values for the NeuVector installation as shown in the sample screen shot below. The YAML presented in the OpenShift Console provides all available configuration options and their default values.
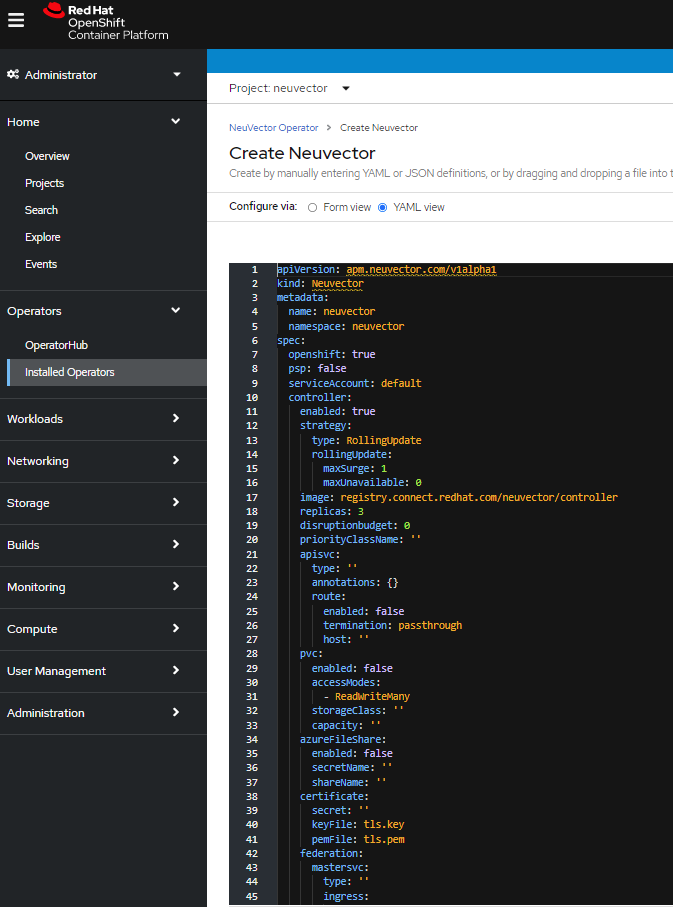
When the operator is installed and ready for use, a NeuVector instance can be installed.
- Click View operator (after the operator installation) or select the NeuVector Operator from the Installed operators view
- Click Create instance
- Select Configure via YAML View
- Paste the prepared YAML configuration values
- Click Create
Verify the installation of the NeuVector instance
- Navigate to the Operator Details of the NeuVector Operator
- Open the NeuVector tab
- Select the neuvector-default instance
- Open the Resources tab
- Verify that resources are in status Created or Running
After you have successfully deployed the NeuVector Platform to your cluster, login to the NeuVector console at https://neuvector-route-webui-neuvector.(OC_INGRESS).
- Login with the initial username admin and password admin.
- Accept the NeuVector end user license agreement.
- Change the password of the admin user.
Optionally, you can also create additional users in the Settings -> Users & Roles menu.
Now you are ready to navigate the NeuVector console to start vulnerability scanning, observe running application pods, and apply security protections to containers.
Upgrading NeuVector
Upgrade the NeuVector version by updating the Operator version which is associated with the desired NeuVector version.
Deploy Using Community Operator
Deploy Using the NeuVector Community Operator from Operator Hub
Technical notes
- NeuVector container images are pulled from Docker Hub from the NeuVector account.
- NeuVector manager UI is typically exposed via an OpenShift passthrough route on a domain. For example, on IBM Cloud neuvector-route-webui-neuvector.(cluster_name)-(random_hash)-0000.(region).containers.appdomain.cloud. It can also be exposed as the service neuvector-service-webui through a node port address or public IP.
- OpenShift version 4.6+
- It is recommendeded to review and modify the NeuVector installation configuration by modifying the yaml values before creating the NeuVector instance. Examples include imagePullSecrets name, tag version, ingress/console access, multi-cluster federation, persistent volume PVC etc. Please refer to the Helm instructions at https://github.com/neuvector/neuvector-helm for the values that can be modified during installation.
Create the project neuvector
oc new-project neuvectorApply security context constraint (SCC) to grant default service account in neuvector namespace to run privileged containers.
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged --serviceaccount default --namespace neuvectorInstall the NeuVector Community Operator from the Operator Hub
- In the OpenShift Console UI, navigate to OperatorHub
- Search for NeuVector Operator and select the listing with the community badge
- Click Install
- Configure update channel. Current latest channel is beta, but may be moved to stable in the future. Select stable if available.
- Configure installation mode and installed namespace
- Select specific namespace on the cluster
- Select neuvector as installed namespace
- Configure approval strategy
- Confirm Install
- Download the Kubernetes secret manifest which contains the credentials to access the NeuVector container registry. Save the YAML manifest file to ./neuvector-secret-registry.yaml.
Apply the Kubernetes secret manifest containing the registry credentials.
kubectl apply -n neuvector -f ./neuvector-secret-registry.yamlPrepare the YAML configuration values for the NeuVector installation starting from the following YAML snippet. Be sure to specify the desired NeuVector version in the 'tag' value. Check the reference of values in the NeuVector Helm chart to get available configuration options. There are other possible Helm values which can be configured in the YAML, such as whether you will configure the cluster to allow multi-cluster management by exposing the Master (Federated Master) or remote (Federated Worker) services.
apiVersion: apm.neuvector.com/v1alpha1
kind: Neuvector
metadata:
name: neuvector-default
namespace: neuvector
spec:
openshift: true
tag: 4.3.0
registry: docker.io
exporter:
image:
repository: prometheus-exporter
tag: 0.9.0
manager:
enabled: true
env:
ssl: true
image:
repository: manager
svc:
type: ClusterIP
route:
enabled: true
termination: passthrough
enforcer:
enabled: true
image:
repository: enforcer
cve:
updater:
enabled: true
image:
repository: updater
tag: latest
schedule: 0 0 * * *
scanner:
enabled: true
replicas: 3
image:
repository: scanner
tag: latest
controller:
enabled: true
image:
repository: controller
replicas: 3When the operator is installed and ready for use, a NeuVector instance can be installed.
- Click View operator (after the operator installation) or select the NeuVector Operator from the Installed operators view
- Click Create instance
- Select Configure via YAML View
- Paste the prepared YAML configuration values
- Click Create
Verify the installation of the NeuVector instance.
- Navigate to the Operator Details of the NeuVector Operator
- Open the NeuVector tab
- Select the neuvector-default instance
- Open the Resources tab
- Verify that resources are in status Created or Running
After you have successfully deployed the NeuVector Platform to your cluster, login to the NeuVector console at https://neuvector-route-webui-neuvector.(INGRESS_DOMAIN).
- Login with the initial username admin and password admin.
- Accept the NeuVector end user license agreement.
- Change the password of the admin user.
- Optionally, you can also create additional users in the Settings -> Users & Roles menu.
Now you are ready to navigate the NeuVector console to start vulnerability scanning, observe running application pods, and apply security protections to containers.
Upgrading NeuVector
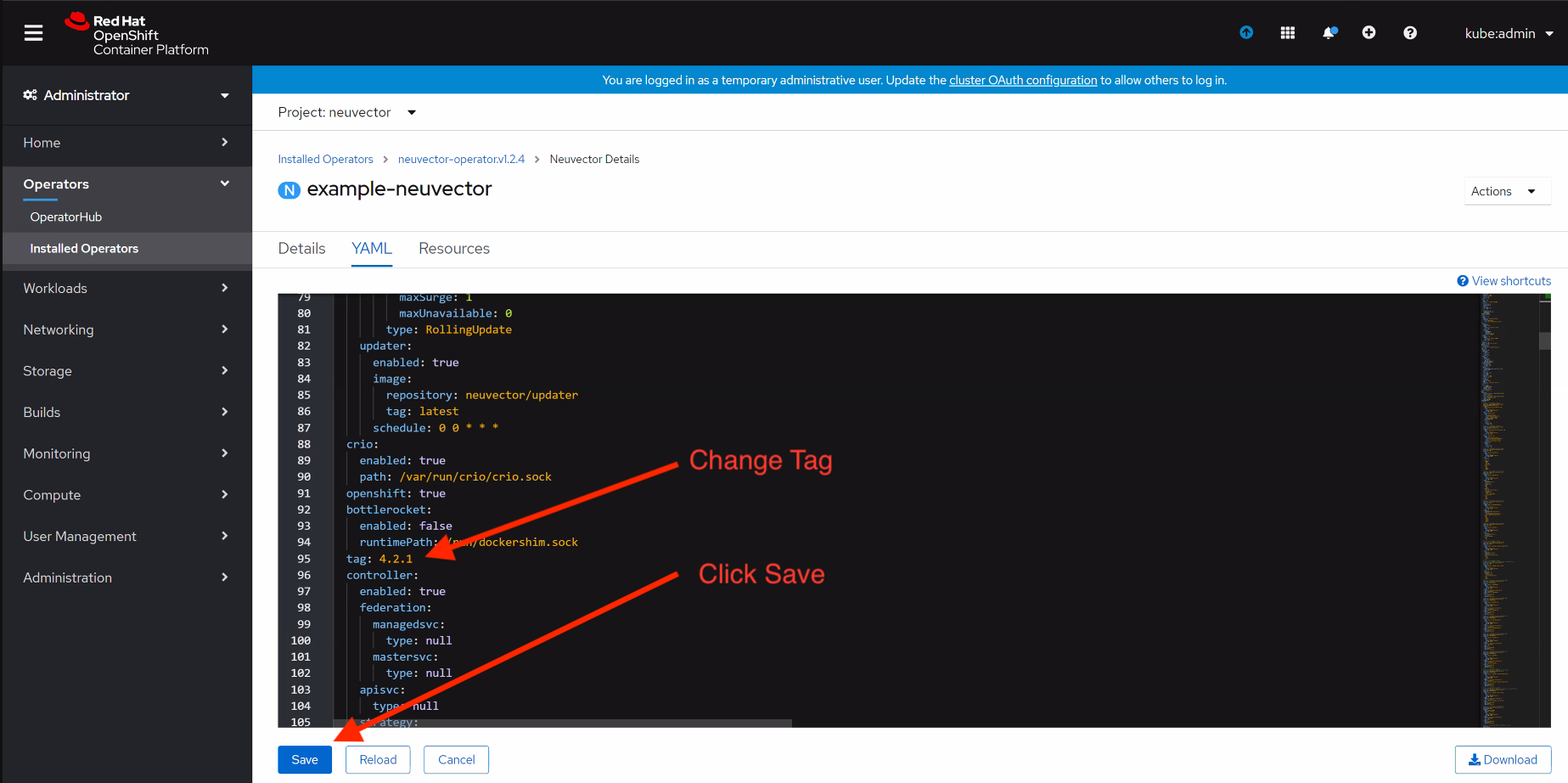
From Operators > Installed Operators > NeuVector Operator
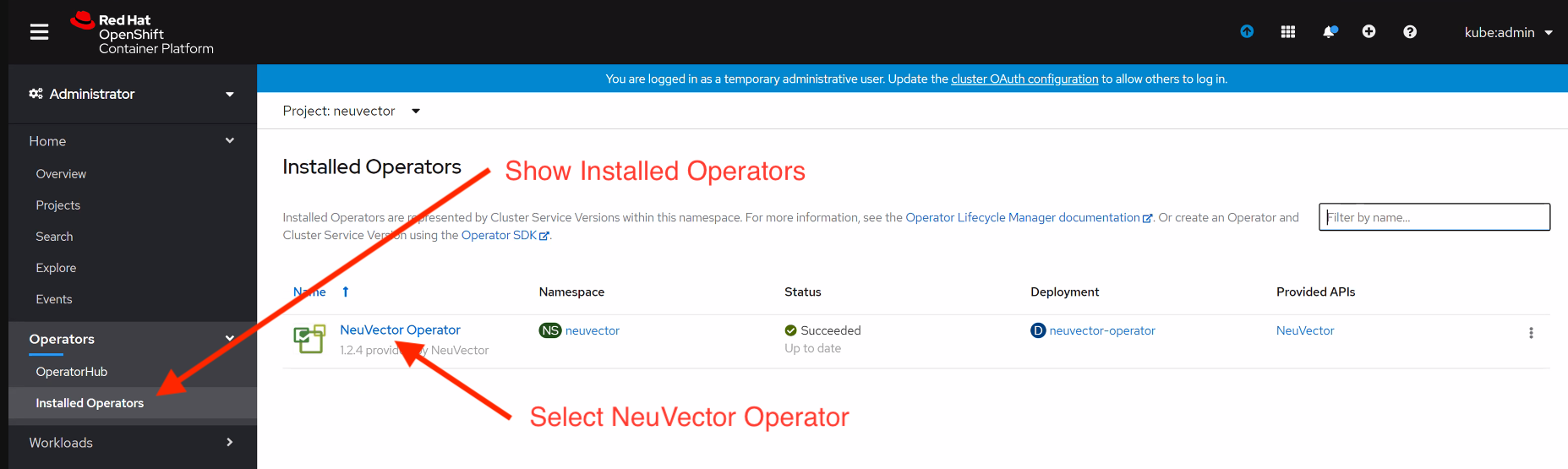
Click on NeuVector to list instances
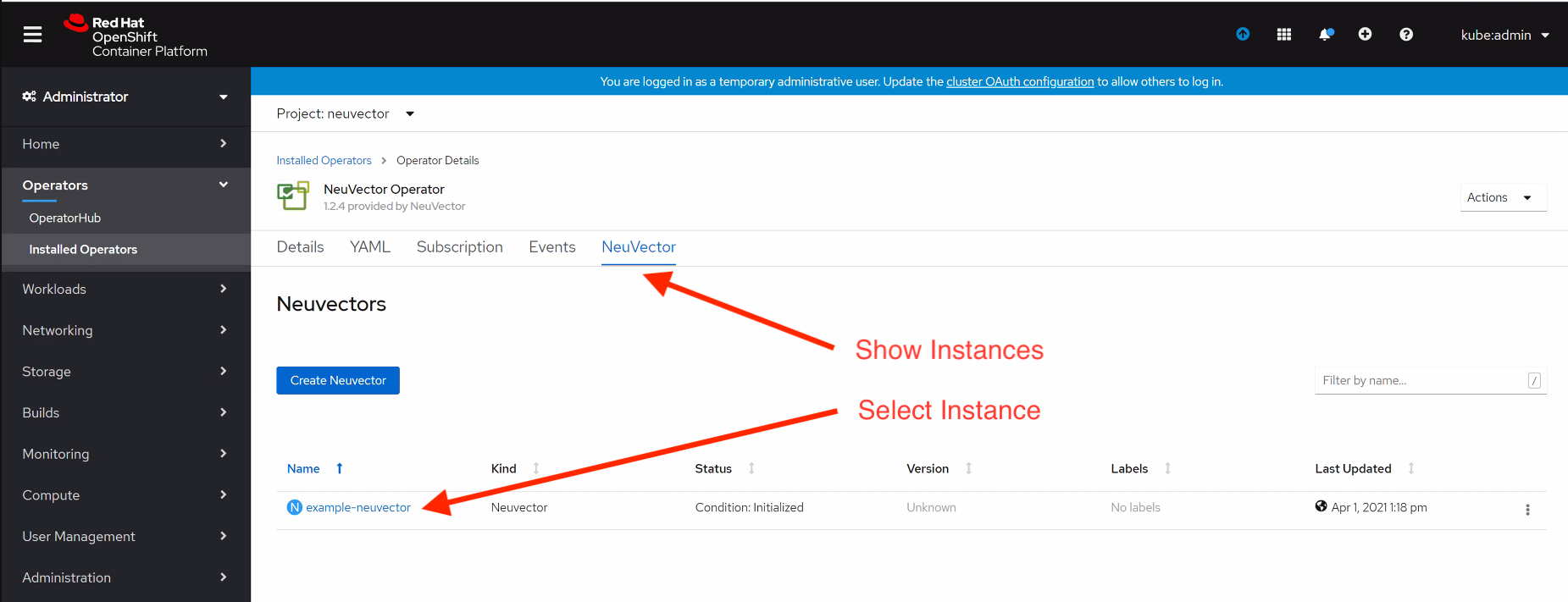
Click on YAML to edit parameters
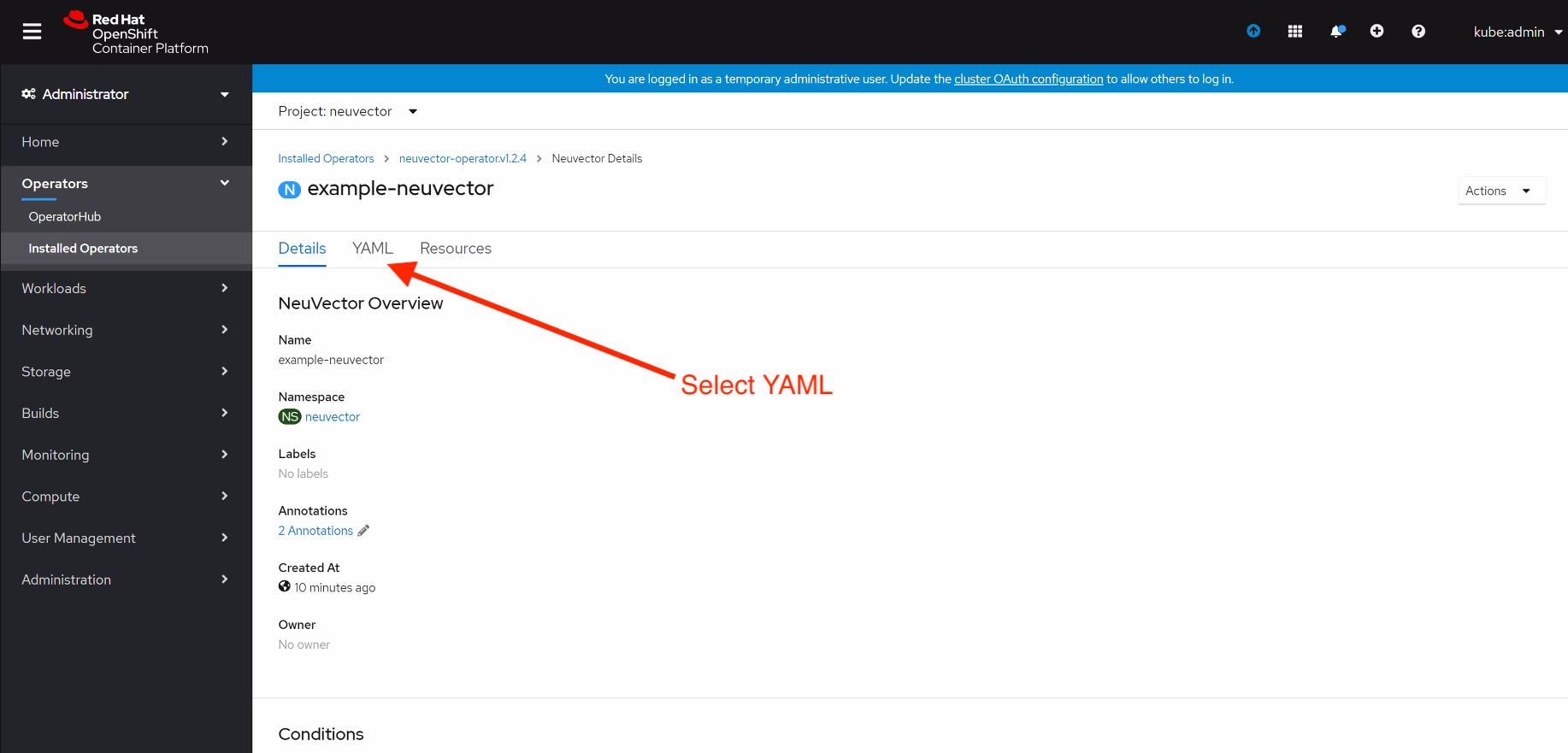
Update tag and click Save
Troubleshooting
- Check the Operator deployment values in the deployed yaml file
- Verify that security context constraint (SCC) for NeuVector in step 2 was successfully added
- Review and check the NeuVector Helm chart values
- Make sure the registry path and version tag is set properly (community operator; certified will use the defaults)
- Make sure the route to the NeuVector manager service neuvector-route-webui is configured